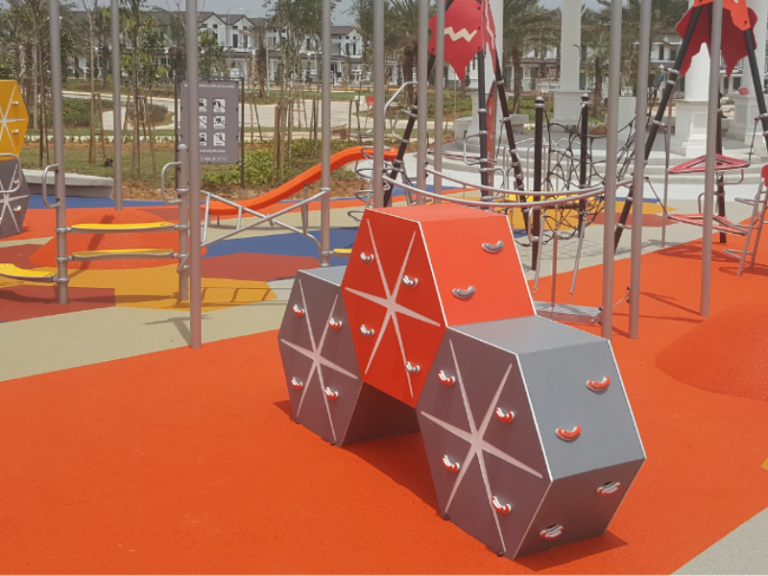
What is Wet Pour?
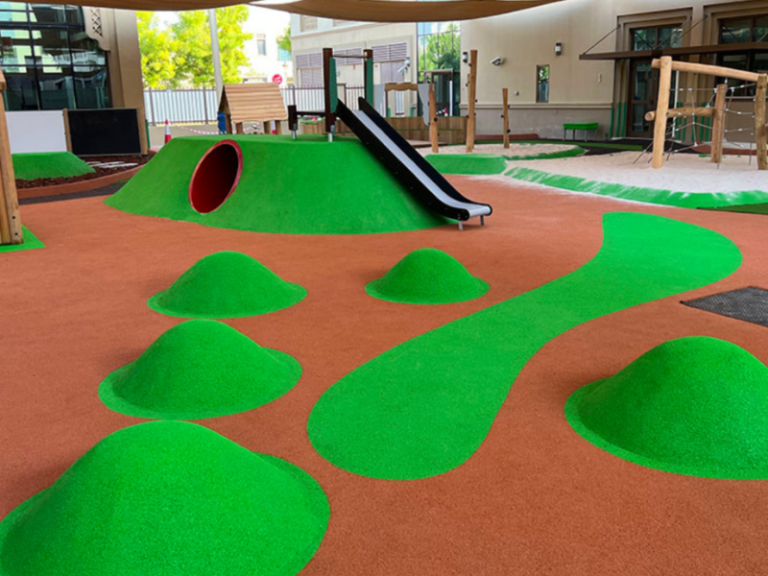
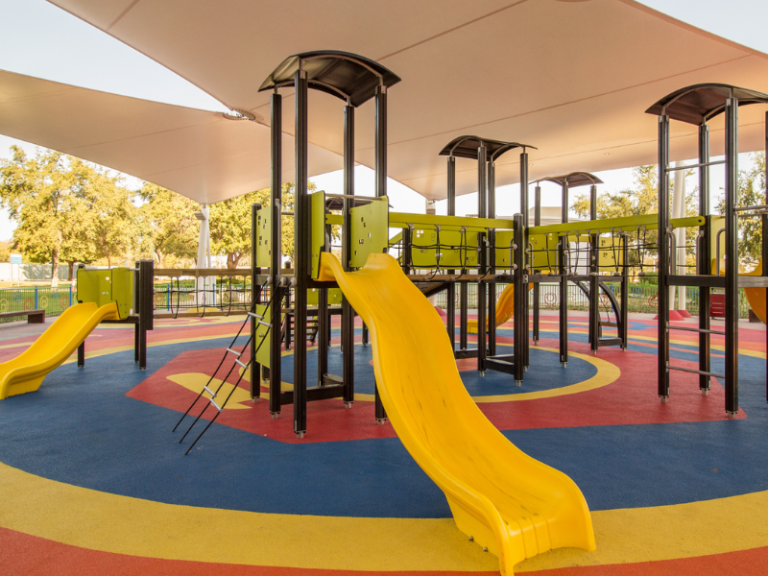
Wet pour is a seamless rubber flooring system made by mixing polyurethane binder with rubber granules, typically used for playgrounds, sports courts, and safety surfaces. This flooring provides excellent shock absorption, slip resistance, and durability, making it ideal for areas with high foot traffic or impact risk. Wet pour surfaces can be customized in various colors and thicknesses to meet specific safety and design requirements. Its low maintenance and weather-resistant properties make it a preferred choice for both indoor and outdoor applications, especially where safety and visual appeal are priorities.



Aromatic Binders vs Aliphatic Binders
Aromatic Binders (Non-UV)

Aromatic binders are widely used in sports flooring due to their affordability and strong bonding capabilities. However, they are non-UV resistant, which means they may yellow or discolor when exposed to direct sunlight. Despite the color change, they maintain excellent mechanical strength, making them a good choice for indoor sports facilities or shaded outdoor areas.
Aliphatic Binders (UV)

Aliphatic binders, on the other hand, are UV-resistant and retain their color over time, even in extreme sunlight. This makes them ideal for outdoor sports flooring installations, especially where vibrant or light-colored EPDM granules are used. Although more expensive, aliphatic binders offer superior weather resistance, durability, and long-term visual appeal.
Wet Pour Installation Process: Step-by-Step Guide
Installing wet pour rubber surfacing involves a precise, multi-step process to ensure durability, safety, and visual appeal. Here’s how it’s done:
1. Site Preparation
The base must be clean, stable, and well-drained. Common bases include concrete, asphalt, or compacted stone sub-base. Any uneven surfaces are leveled to ensure proper bonding.
2. Edging Installation
Timber, concrete, or rubber edging is installed to define the area and contain the wet pour material during the pouring and curing process.
3. Primer Application (if needed)
A PU primer may be applied to help bond the wet pour system to the sub-base, especially on porous or dusty surfaces.
4. Binder & Rubber Mixing
EPDM or SBR rubber granules are mixed on-site with a polyurethane binder (either aromatic or aliphatic) using a forced action mixer. The mixture must be uniform and workable before spreading.
5. Wet Pour Application
The mixed material is poured onto the surface and evenly spread using screeds and hand trowels, maintaining consistent thickness—commonly 15–40mm depending on usage and safety requirements.
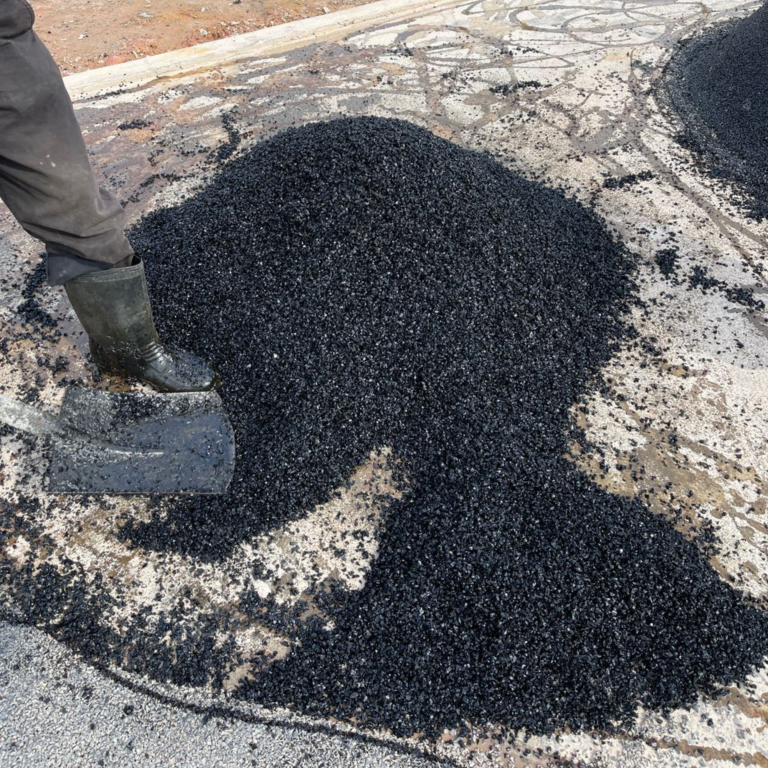

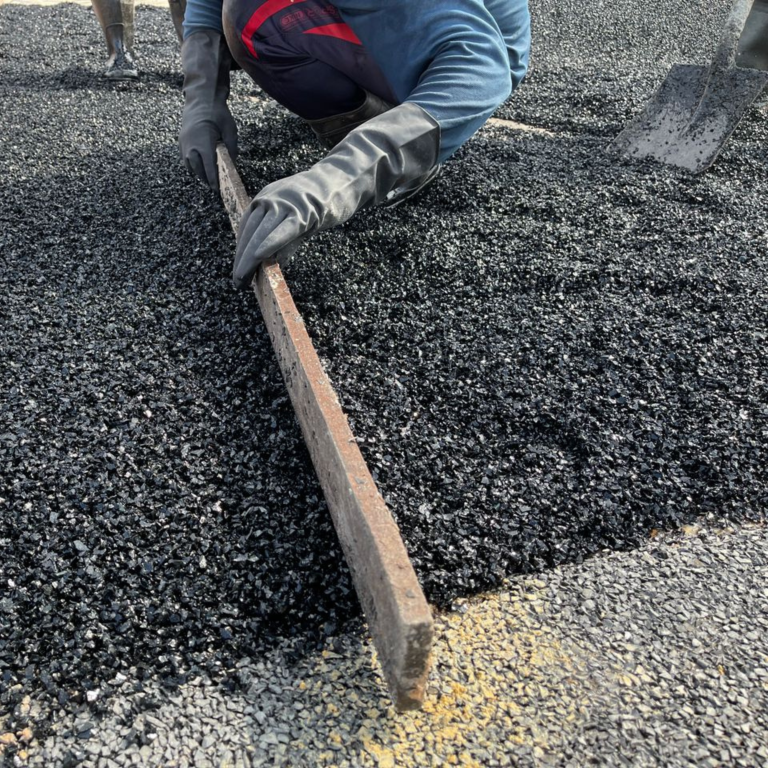
6. Finishing Touches
Installers smooth out the surface carefully to avoid uneven patches or air pockets. Custom designs, colors, or patterns may also be incorporated at this stage.

7. Curing Time
The surface must cure undisturbed for 24–48 hours depending on weather conditions. Proper curing ensures maximum strength and elasticity.
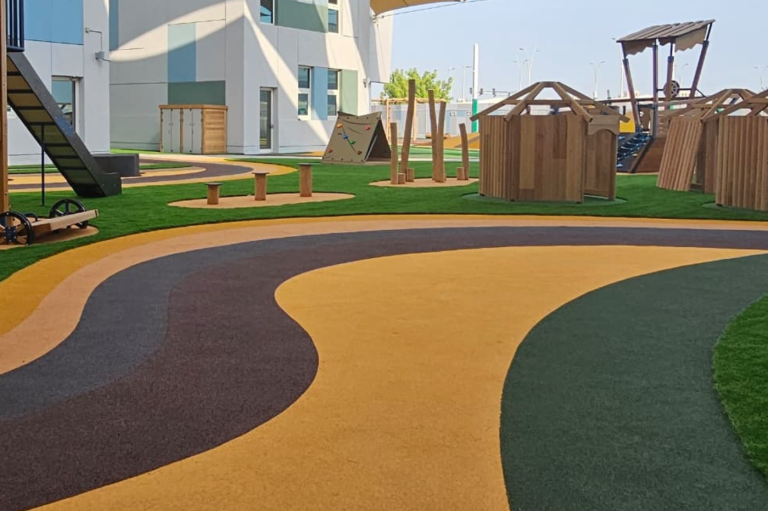

Tip: Avoid installation during rain or extreme heat to prevent poor curing or binder failure.
Summary
| Feature | Aromatic | Aliphatic |
|---|---|---|
| UV Stability | Non?UV resistant – yellows under sunlight | UV resistant – minimal discoloration |
| Appearance | Tends to amber yellow, especially on light EPDM | Retains original color and vibrancy |
| Cost | More budget-friendly and widely used | Higher cost but premium aesthetic value |
| Ideal Use Cases | Indoor courts, shaded areas, cost-conscious installs | Outdoor playgrounds, tracks, high-visibility sports flooring |